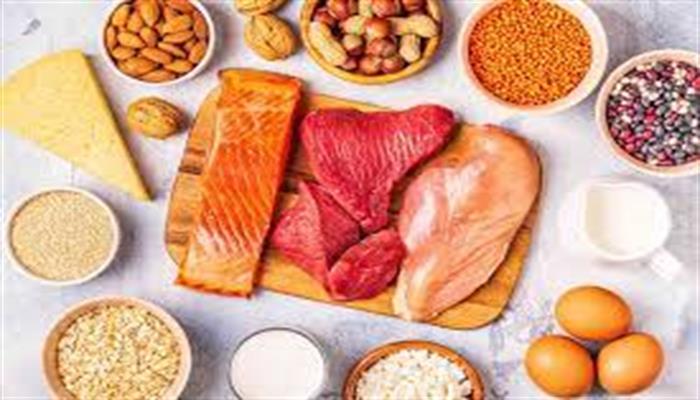
Low carb, high protein diets restrict people’s consumption of carbohydrates, such as bread, while promoting a higher-than-usual consumption of proteins, such as lean meats. This type of eating plan may be beneficial for weight loss and muscle building, but it may also carry a few health risks.
Protein, carbohydrates, and fats are macronutrients. These nutrients are necessary in large quantities to provide a person with energy and keep them healthy.
It is important for a person to have a balanced diet and consume sufficient amounts of each macronutrient. However, if a person is looking to lose weight or alter their body composition, they may wish to adjust the balance of their macronutrients and consume more protein while reducing their carbohydrate intake.
In this article, we discuss the roles of carbohydrates and protein in the diet. We also explain what foods are high in protein and low in carbs and suggest a meal plan that people can try.
Role of protein and carbohydrate in the diet

Protein is a major component of the skin, muscle, bone, organs, hair, and nails. Dietary protein is important for preventingTrusted Source lean body mass loss, promoting growth and repair of the body, and generally maintaining good health. Dietary protein may come from animal sources or plant-based foods.
Carbohydrates act as the body’s main energy source and can be either simple or complex. These types of carbohydrates differ in chemical structure and the speed at which the body absorbs them. Simple carbohydrates contain one or two sugar molecules, and the body absorbs them more quickly than complex carbohydrates, which have a longer molecular chain.
Dietary guidelines suggest the following carbohydrate and protein intake for male and female adults:
| Sex | Female | Female | Female | Male | Male | Male |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 19–30 | 31–50 | 51+ | 19–30 | 31–50 | 51+ |
| Calorie Intake | 2,000 | 1,800 | 1,600 | 2,400 | 2,200 | 2,000 |
| Recommended protein intake (% of calories) | 10–35 | 10–35 | 10–35 | 10–35 | 10–35 | 10–35 |
| Recommended carbohydrate intake (% of calories) | 45–65 | 45–65 | 45–65 | 45–65 | 45–65 | 45–65 |
To follow a low carbohydrate, high protein diet, a person would need to drop their carb intake to about 26%Trusted Source of their total calories. The definition of a high protein intake varies among sources, but one study trialing a high protein diet defined it as 30% of a person’s total calorie intake.
Benefits
A low carb, high protein diet may offer several benefits, including:
- Weight loss: There is some evidenceTrusted Source to suggest that a low carb, high protein diet may facilitate weight loss. This result is due in part to protein helping people feel fuller with less food. However, the results will vary depending on various factors, including calorie consumption and amount of exercise.
- Maintain weight loss: In addition to facilitating weight loss, a high protein diet may help people maintainTrusted Source a lower body weight.
- Body Composition: Body composition refers to the percentage of fat, bone, water, and muscle in the human body. Research suggests that diets high in protein may improve body composition.
- Blood Sugar: A 2019 study looking at a reduced carbohydrate, high protein diet for people with type 2 diabetes notes that this way of eating improved average glucose levels.
- Heart Disease: Low carbohydrate diets may have a beneficial effectTrusted Source on factors that contribute to heart disease. However, more research is necessary to establish the long-term effects of a low carb diet on heart health.
- Bone health: A 2019 meta-analysis highlights that eating more protein than the average recommended daily allowance can reduce the risk of hip fracture and loss of bone mineral density in older adults.
Risks
Adopting a low carb, high protein diet may pose certain risks. For example, a diet that is high in protein can put acid loadTrusted Source on the kidneys, which may increase a person’s risk of developing kidney disease.
An older reviewTrusted Source suggests that the long-term consumption of a high protein diet may also contribute to the following health issues:
- bone disorders
- increased cancer risks
- problems with liver function
- coronary artery disease
A 2018 studyTrusted Source notes that the type of protein that a person consumes on a low carb, high protein diet may affect mortality. Low carb diets that incorporate protein and fat from meats, such as chicken, pose a higher mortality risk than plant-based proteins and fats.
A person should consider consulting their doctor before making any radical dietary changes. They may also wish to work with a dietitian to create an eating plan.
Foods to include
People following a low carb, high protein diet can include the following foods in their meals:
- eggs
- fish and shellfish
- meat
- poultry
- certain dairy
- nonstarchy vegetables
- seeds
- soy
- mycoprotein
Foods to avoid
People who are trying to limit their carbohydrate intake may wish to avoid the following types of foods:
- bread and grains
- starches
- sugary drinks
- processed high carb foods
- cereal
- certain alcohols
- juice
Supplements
A person can also increase the amount of protein in their diet by taking supplements, although it is advisable to discuss this with a doctor first. Protein supplements include:
- Whey isolate: Whey is a byproduct of milk, and it is often a core ingredient in protein shakes. Whey isolate has undergone a process to remove fats and carbs, leaving mostly protein. A person can mix whey isolate powder with milk or water.
- Vegan isolate powder: Products with vegan isolate powder often use pea or bean isolate. Similar to whey isolate, a person can mix vegan isolate powder with a plant-based milk or water.
- Protein bars: These are often a useful snack when on a low carb, high protein diet. However, a person should check the nutrients, as protein bars vary in the amount of carbs and protein they contain.
- Protein capsules: These are pills that contain protein powder. Depending on the manufacturer, the capsules may use different types of protein powder.
Meal plan example
Below is an example of a low carb, high protein meal plan:
- Breakfast: spinach omelet or scrambled tofu
- Snack: cucumber strips wrapped in chicken slices or hummus with carrot batons
- Lunch: seasoned grilled chicken or tempeh with cauliflower rice and vegetables, such as broccoli or oven baked carrots and zucchini
- Snack: whey isolate or a vegan protein shake
- Dinner: grilled turkey or vegan burger with a salad containing cucumber, tomato, and feta or a cheese alternative
- Snack: boiled egg or a small handful of seeds and nuts
Summary
Protein and carbohydrates are important macronutrients that provide the body with energy and support good health. A diet that is low in carbs but high in protein may help facilitate weight loss and improve body composition.
However, this eating plan can negatively affect the liver and kidneys, and more research is necessary to understand its long-term effects on health. A person should consult a doctor before making drastic changes to their diet.
Referance: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com